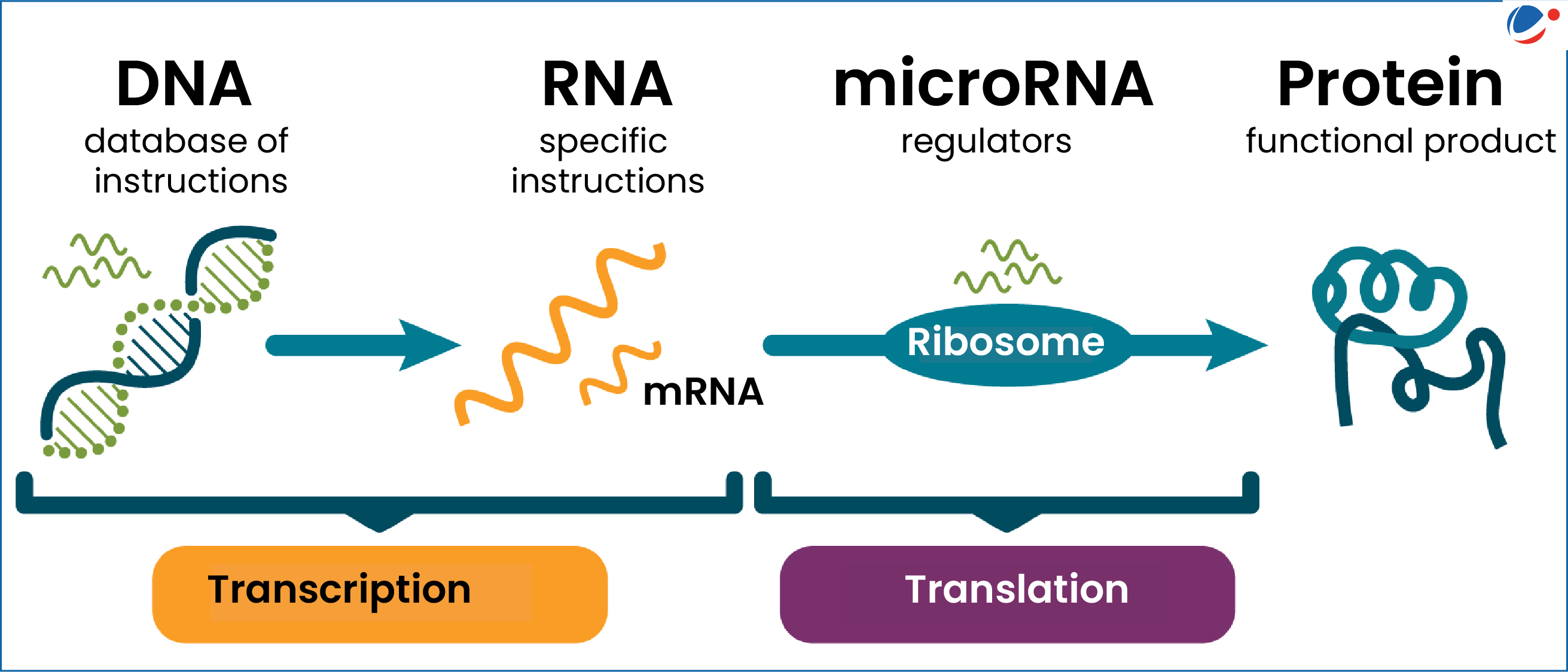
The discovery of microRNA has transformed our understanding of gene regulation, revealing a sophisticated layer of control over gene expression that was previously unknown. Pioneered by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun and his collaborator Victor Ambros in 1992, this groundbreaking research utilized the C. elegans roundworm to uncover the pivotal role that these tiny RNA molecules play in cellular processes. Initially met with skepticism, their findings eventually demonstrated the universal relevance of microRNA across diverse organisms, including humans, and earned them the prestigious Nobel Prize in 2024. As RNA research continues to evolve, the implications of microRNAs extend far beyond basic science, holding promise for novel therapeutic approaches to diseases like cancer, heart conditions, and neurodegenerative disorders. The journey from their modest discovery to becoming fundamental players in the world of gene regulation showcases the power of scientific inquiry and innovation.
MicroRNA research stands at the forefront of molecular biology, exploring the intricate mechanisms through which small RNA molecules regulate genetic activity. This avenue of investigation has highlighted how microRNAs contribute to various developmental and physiological functions, providing insights that extend across multiple forms of life. Leveraging model organisms like *Caenorhabditis elegans*, scientists have been able to elucidate how these regulatory molecules influence gene expression at a fundamental level. As the field continues to expand, it opens up new frontiers in medical research and therapeutic applications, reinforcing the importance of understanding RNA dynamics in health and disease. The groundbreaking work of researchers such as Gary Ruvkun has forever altered our perspective on genomic regulation, marking a pivotal shift in biomedical science.
The Pioneering Research of Gary Ruvkun
Gary Ruvkun’s groundbreaking work is at the heart of modern gene regulation discovery, particularly the study of microRNAs. In 1992, his collaborative research with Victor Ambros focused on the tiny yet impactful molecules in the C. elegans roundworm, which led to significant revelations about cellular processes across various species, including humans. Despite initial skepticism from the evolutionary biology community, Ruvkun’s findings with microRNA have paved the way for new understandings of gene expression, influencing research paradigms in RNA biology.
Ruvkun’s insights did not happen in a vacuum; they emerged from years of persistence and scholarly investigation. His lab was primarily supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants, which allowed him to focus on fundamental research even when it faced reluctance from broader scientific audiences. This dedication has ultimately transformed how scientists perceive tiny RNAs, marking a pivotal shift in the field of genetics and highlighting Ruvkun’s important role in establishing microRNA discovery as a crucial area of study.
Ruvkun’s exploration into microRNAs is deeply intertwined with the evolution of gene regulation mechanisms. Initially, the implications of microRNA disproved the long-standing notion that all RNA serves merely as a messenger for protein synthesis. Instead, these small but vital molecules have been recognized for controlling gene expression and addressing organismal development complexity, solidifying Ruvkun’s legacy within genomic research.
The gradual acceptance of Ruvkun’s findings reflects a significant evolution within the scientific community, transitioning from skepticism to a broad consensus acknowledging microRNAs as fundamental to understanding genetics. As more researchers invest their efforts in RNA studies, Ruvkun’s early suspicions of the importance of microRNAs have proven to be revolutionary, influencing countless areas of biomedicine and molecular engineering.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is microRNA discovery and why is it significant in gene regulation?
MicroRNA discovery refers to the identification of small RNA molecules that play crucial roles in gene regulation. This concept was first revealed by Nobel laureates Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the early 1990s during their research on the C. elegans roundworm. MicroRNAs regulate gene expression by binding to messenger RNA, influencing protein production, which is fundamental to understanding developmental and physiological processes in organisms.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to the field of microRNA research?
Gary Ruvkun, alongside Victor Ambros, made pioneering contributions to microRNA research by discovering these small RNA molecules in the C. elegans model organism. Their work, published in 1993, showcased a new layer of gene regulation, ultimately leading to the understanding that microRNAs are vital in both plant and animal biology. This groundbreaking research earned them the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024.
What are the potential therapeutic applications of microRNA research?
MicroRNA research has led to promising therapeutic applications in various diseases. Current clinical trials are exploring the use of microRNAs as treatments for heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s Disease, and Alzheimer’s. These tiny RNA molecules play a significant role in regulating gene expression, making them potential targets for innovative therapies aimed at controlling disease processes.
Why was the discovery of microRNAs initially overlooked by the scientific community?
Initially, the discovery of microRNAs by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros was not widely appreciated because the significance of their findings in C. elegans was unclear to many in the evolutionary biology community. Other researchers were skeptical about the relevance of microRNAs to other species, including humans. It wasn’t until years later that the broader implications of this discovery for understanding gene regulation and disease became evident.
How has the perception of microRNAs changed since their discovery in 1992?
Since their discovery in 1992, the perception of microRNAs has dramatically changed. Originally seen as a niche area of research, microRNAs have now become a central focus in molecular biology, impacting various disciplines. The growth of interest in the RNA research community and advancements in our understanding of microRNAs’ roles in gene regulation have established them as fundamental elements in both basic and applied biomedical research.
What role do microRNAs play in regulating human genes?
MicroRNAs play a critical role in regulating human genes by controlling the expression of approximately 1,000 microRNAs found in the human genome. These tiny RNA molecules influence the translation of messenger RNA into proteins, ensuring proper cellular function and development. Disruptions in microRNA activity can lead to a variety of diseases, highlighting their importance in human health.
What was the impact of federal funding on microRNA research according to Gary Ruvkun?
Gary Ruvkun emphasizes the vital role of federal funding in supporting microRNA research. He states that about 75% of his lab’s research has been funded by the federal government over the past 40 years. This consistent financial support has been crucial for advancing discoveries in RNA biology, leading to significant breakthroughs in both basic science and medical applications.
What recognition did Gary Ruvkun achieve for his work on microRNAs?
Gary Ruvkun received the prestigious Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024 for his groundbreaking work on the discovery of microRNAs. This recognition highlights the importance of his contributions to the understanding of gene regulation, demonstrating how fundamental research can lead to profound advancements in our knowledge of biology and medicine.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, which was recognized with the 2024 Nobel Prize. |
| Initial Reception | The discovery was not initially taken seriously by the evolutionary biology community, and it took time for its significance to be acknowledged. |
| Research Funding | Most of Ruvkun’s research has been funded by National Institutes of Health, highlighting the role of federal funding in scientific research. |
| Impact of microRNAs | MicroRNAs play a key role in gene regulation across species, including humans, affecting various diseases. |
| Clinical Trials | Therapies based on microRNAs are currently in clinical trials for treating diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s. |
| Technological Influence | Research from microRNA studies has contributed to the growth of major companies like Alnylam focusing on RNA therapeutics. |
| Concern for Future Research | Ruvkun is worried that cuts in federal funding could hinder scientific progress and drive young researchers to seek opportunities abroad. |
Summary
MicroRNA discovery represents a pivotal advancement in the field of genetics, revealing intricate layers of gene regulation previously unknown to science. The research conducted by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros has transformed our understanding of how microRNAs influence development, health, and disease. Their work underscores the importance of sustained funding for scientific research, as it not only leads to groundbreaking discoveries but also drives innovation within the biotechnology sector. As therapies for various diseases derived from microRNA research move into clinical trials, the value of understanding microRNA functions grows ever clearer, presenting new possibilities for therapeutic interventions.